
Specialize in Compression molds

Specialize in Compression molds
A recent computational analysis demonstrates that DMLS-produced metal molds—featuring honeycomb internal structures—can meet the structural and thermal demands of compression molding while reducing material usage by up to 74% compared to conventionally machined molds. This breakthrough has direct implications for high-precision SMC mold, compression mold, and advanced composite tooling applications.
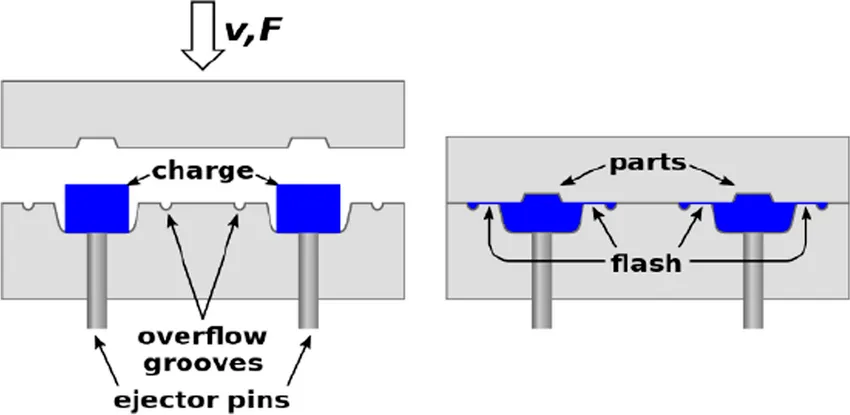
Traditional compression mold fabrication relies on subtractive machining—CNC milling, turning, and EDM—to produce high-precision tooling. While accurate, these methods incur long lead times, high tooling steel consumption, and substantial material waste. The computational study summarized here evaluates Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) as an alternative production route for compression mold tooling. Key findings include:
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) is a powder-bed fusion metal additive manufacturing technology that constructs parts layer-by-layer using a focused laser to fuse metal powder. For compression mold and SMC mold manufacturers, DMLS offers several strategic advantages:
Additive lattice and honeycomb designs drastically reduce the volume of expensive tool steel required for large molds. The reported 74% material savings translate directly into lower material cost and reduced machining allowance when hybrid finishing (DMLS + CNC) is applied.
DMLS enables features that are difficult or impossible to machine: internal lattices for light-weighting, integrated conformal cooling channels for thermal uniformity, and topology-optimized ribs that maximize stiffness per unit mass—capabilities that are especially beneficial for high-volume compression tooling.
For R&D, prototype molds, or low-volume specialized tools, DMLS reduces lead times by removing complex multi-step machining processes. Iterations—such as channel geometry or reinforcement—can be implemented directly in the CAD model and printed without the need for expensive fixturing changes.
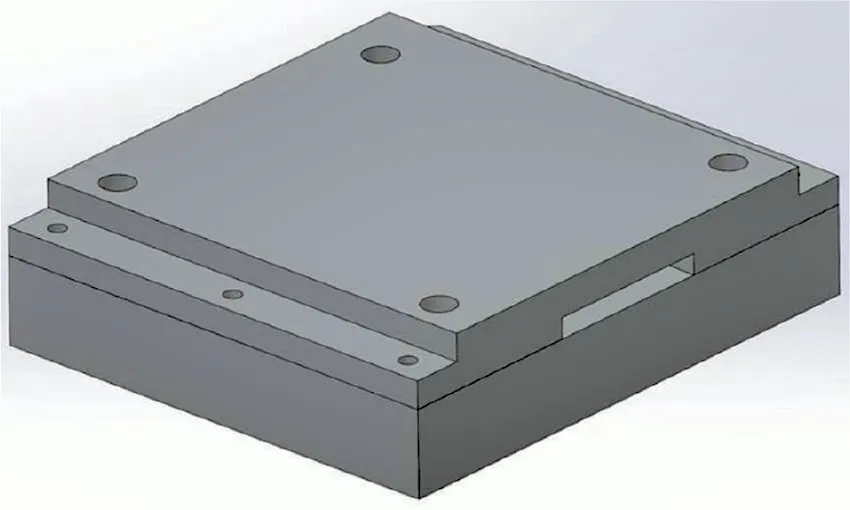

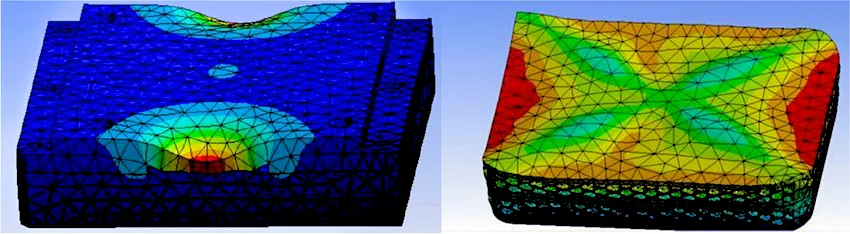
The study compared two mold concepts under identical molding conditions: a solid machined steel mold (reference) and a DMLS-manufactured mold with a honeycomb internal structure. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) evaluated mechanical deflection under molding pressure and thermal gradients representative of SMC compression cycles.
Using linear and non-linear static simulations, the DMLS honeycomb mold maintained a maximum deflection below the stringent tolerance of 0.001 inches. The lattice geometry was tuned to concentrate material along principal stress paths while removing mass in low-stress regions.
Transient thermal simulations modeled heat input during a typical compression-curing cycle and subsequent cooling. The DMLS mold’s lower thermal mass (due to internal cavities) required active thermal management—implemented via conformal cooling channels—to ensure uniform cure and avoid hot spots. With conformal cooling, temperature differentials were within acceptable process windows.
The research emphasized a hybrid workflow: DMLS for the internal topology and near-net shape plus precision CNC finishing on critical mating surfaces. This approach ensures required surface finish and dimensional tolerances, while still preserving the material and time advantages of additive production.
Based on computational results and best practices, the following guidelines are recommended when applying DMLS to compression mold tooling:
While DMLS reduces raw material waste, manufacturers must evaluate machine time, powder costs, and post-processing expenses. Key considerations include:
Practical conclusion: For mid-to-high complexity molds and R&D tooling, DMLS (combined with CNC finishing) is often economically and technically superior. For simple, very large-volume tooling with minimal internal features, traditional machining may still be preferable.
For a composite tooling specialist like MDC Mould, DMLS represents a strategic technology to complement existing CNC and EDM capabilities. Specific opportunities include:
Adopting DMLS helps MDC strengthen its service offering for automotive SMC body panels, EV enclosures, structural composite parts, and specialized thermoforming tooling.
This computational study demonstrates that DMLS is a technically viable option for modern compression mold manufacturing. When combined with conformal cooling and hybrid finishing strategies, DMLS molds can meet the strict structural and thermal demands of SMC compression processes while delivering substantial material savings and enhanced design freedom. For SMC mold and composite tooling providers, integrating DMLS into the manufacturing mix will open new possibilities for performance, sustainability, and rapid iteration.
Contact MDC Mould to learn how we integrate additive manufacturing with precision CNC finishing for next-generation compression molds: Contact us.
Core keywords: DMLS, compression mold, SMC mold, composite tooling, metal additive manufacturing, honeycomb mold, conformal cooling.
Contact US
Email: master@zjmdc.com
Tel: +86 576 84616076
Fax: +86 576 84616079
Mobile: +86 13906573507(Mr. Wang)
Address: No.116 mochuang road, Huangyan Xinqian street,Taizhou,Zhejiang,China