What is compression molding? Compression molding is a process of molding in which a composite material is placed into an open, heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed with a top plug and compressed with large hydraulic presses in order to have the material contact all areas of the mold. The charge cures in the heated mold. After the material has hardened, remove it from the cavity. This guide provides you the basics about compression molding.
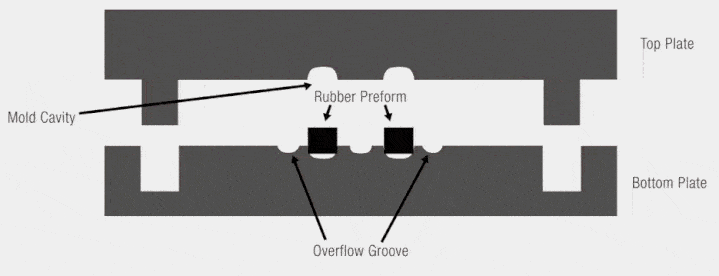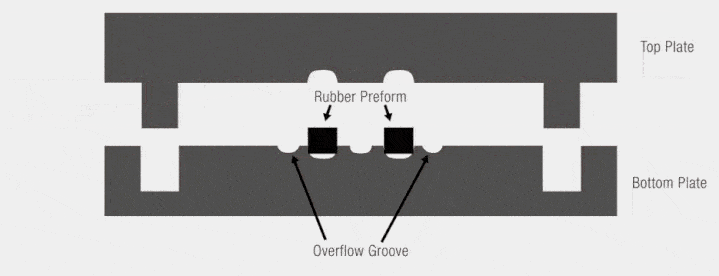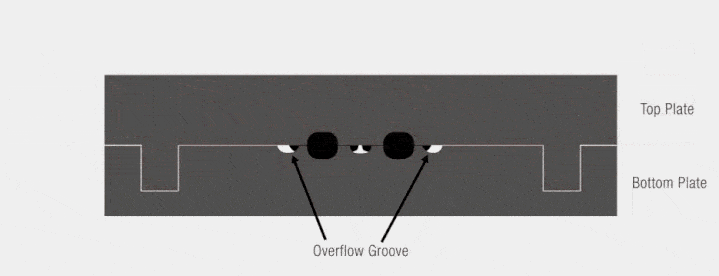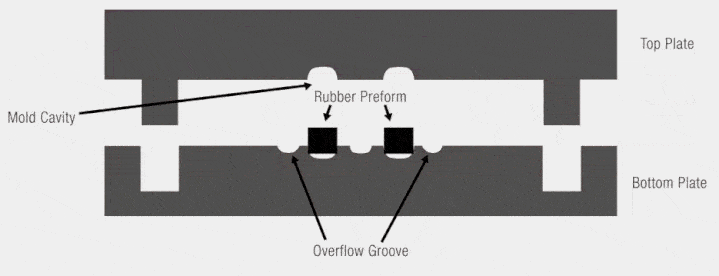
compression molding animation
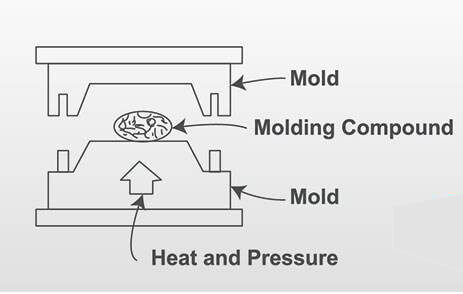 Overview of Compression Molding
Overview of Compression Molding
Compression molding is a method of adding a premix or prepreg to a mold and molding a composite material product by heating and pressing, which belongs to high-pressure molding. According to the different impregnation methods of the matrix and the reinforcing material in the molding material, the molding process can be divided into two categories: one is that the resin and the reinforcement are added to the cavity at the same time, which is called wet compression molding; the other is that the resin has been combined with Reinforcement materials are mixed and impregnated to prepare molding materials, which are directly added to the mold cavity during molding, which is called dry or semi-dry molding. Most compression molding uses a dry or semi-dry process. Compression molding is to first put the composite material into the mold, and after the mold is closed by the press, the molded material is heated and plasticized in the mold cavity, flows under pressure and fills the mold cavity, and then cooled and demolded to obtain the product.
Seven steps of compression molding
Compression Moulding is a method of moulding in which the moulding material, generally preheated, is first placed in an open, heated mould cavity. The mould is closed with a top force or plug member, pressure is applied to force the material into contact with all mould areas, while heat and pressure are maintained until the moulding material has cured. The seven steps of compression moulding are as follows
-
#1: feed material: The initial charge of molding compound can be in any of several forms, including powders or pellets, liquid, or preform. The amount of polymer must be precisely controlled to obtain repeatable consistency in the molded product. It has become common practice to preheat the charge prior to its placement into the mold; this softens the polymer and shortens the production cycle time. Preheating methods include infrared heaters, convection heating in an oven, and use of a heated rotating screw in a barrel. The latter technique (borrowed from injection molding) is also used to meter the amount of the charge. Add a specified amount of material into the mould as needed, and the amount of feeding directly affects the density and size of the product. If the amount of feed is large, the product has thick burrs, poor dimensional accuracy, and it is difficult to demold and may damage the mould; if the amount of feed is small, the product is not tight, the gloss is poor, and even a lack of material results in scrap.
-
#2: Mould closing: Even after the feeding, the male and female moulds are closed. Use fast when closing the mould, wait for the negative, and change to the slow speed when the male mould is in quick contact. The operation method of quick first and slow second is helpful to shorten the non-production time, prevent the mould from scratching, avoid the raw material in the mould groove being taken out by the air due to too fast clamping, and even displace the insert and damage the moulding rod. After the mould is closed, the pressure can be increased to heat and pressurize the raw materials.
-
#3: Exhaust: When molding thermosetting plastics, water and low-molecular substances are often released. In order to exclude these low-molecular substances, volatiles, and air in the mould, the plastic reaction in the mould cavity of the compression mould can be carried out until the appropriate time. Exhaust the pressure to release the mould for a short period of time. Exhaust operation can shorten the curing time and improve the physical and mechanical properties of the product, avoiding the occurrence of delamination and bubbles inside the product; but exhausting too soon, sooner or later, not too early to the purpose of exhaust; too late, because the surface of the material has solidified gas can not be discharged.
-
#4:Curing: The curing of thermosetting plastics is maintained at the moulding temperature for a period of time so that the polycondensation reaction of the resin reaches the required cross-linking degree so that the products have the required physical and mechanical properties. Plastics with a low curing rate can also be temporarily ended when the product can be completely demolded, and then use post-processing to complete the entire curing process; to improve the utilization rate of the equipment. Moulding and curing time is usually pressure holding and holding time, generally ranging from 30 seconds to several minutes, most of which does not exceed 30 minutes. Too long or too short curing time will affect the performance of the product.
-
#5: Demoulding: Demoulding is usually done by ejecting the rod. Products with forming rods or some inserts should first use special tools to remove the forming rods, etc., and then demold.
-
#6: Mould blowing: After demoulding, usually use compressed air to blow the cavity and the mould surface of the mould. If the fixed objects on the mould are tight, you can also clean them with a copper knife or a copper brush, and even use a polishing agent.
-
#7: Post-treatment: In order to further improve the quality of products, thermosetting plastic products are often post-treated at a higher temperature after demolding. Post-treatment can make the plastic curing more complete; at the same time reduce or eliminate the internal stress of the product, reduce the moisture and volatiles in the product, etc., which is conducive to improving the electrical performance and strength of the product
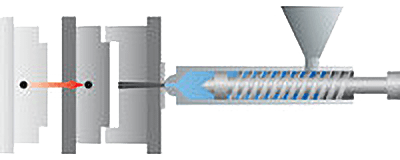
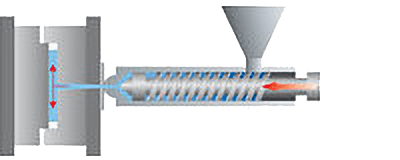


Compression Molding Machines
The equipment used is mainly a press, which is divided into a mechanical type and a hydraulic type. At present, the hydraulic type is mainly used, with tonnages ranging from tens of tons to thousands of tons.

Compression molding material types
What materials can you compression molding? There are many types of compression molding materials, which can be prepreg materials, pre-mixed materials, or blanks. The main types of molding materials currently used are: short fiber molding material, sheet molding compound (SMC), bulk molding compound (BMC), prepreg, glass fiber felt reinforced thermoplastic sheet (GMT), long fiber thermoplastic pellets (LFT-G), etc. Thermoset composites are the most common type of material used in compression molding.
Synthetic resin
The molding compound used for composite molded products requires that the synthetic resin has: ① good wetting properties to the reinforcement material, so as to form a good bond at the interface between the synthetic resin and the reinforcement material; ② has an appropriate viscosity and good fluidity, in the pressing conditions, it can fill the entire cavity with the reinforcing material uniformly; ③ Under the pressing conditions, it has an appropriate curing speed, and there are no by-products or fewer by-products during the curing process, and the volume shrinkage is small; ④ It can meet the specific requirements of the molded product Performance requirements. According to the above selection requirements, commonly used synthetic resins are unsaturated polyester resins, epoxy resins, phenolic resins, vinyl resins, furan resins, silicone resins, polybutadiene resins, allyl esters, melamine resins, Polyimide resin, etc. In order to make the molded products reach specific performance indexes, after selecting the resin type and brand, the corresponding auxiliary materials, fillers, and pigments should also be selected.
Reinforced materials
The commonly used reinforcing materials in molding materials mainly include glass fiber cutting wire, untwisted roving, twisted roving, continuous glass fiber bundle, glass fiber cloth, glass fiber felt, etc., as well as a small number of special products asbestos, felt, asbestos fabric (cloth) and asbestos paper and varieties of high silica fiber, carbon fiber, organic fiber (such as aramid fiber, nylon fiber, etc.) and natural fiber (such as linen, cotton cloth, smelted cloth, non-smelted cloth, etc.). Sometimes two or more fiber mixtures are also used as reinforcement materials.
Auxiliary materials
It generally includes auxiliary materials such as curing agent (initiator), accelerator, diluent, surface treatment agent, low shrinkage additive, mold release agent, colorant (pigment), and filler.
Compression molding Or Injection molding?
Injection molding can produce plastic parts with complex structures. But, the strength of products is not enough, while compression molding allows longer fiber materials with very good strength and toughness. Compression molds are generally simpler than their injection mold counterparts. There is no sprue and runner system in a compression mold and the process itself is generally limited to simpler part geometries due to the lower flow capabilities of the starting thermosetting materials. Compared to injection molding, it produces fewer braided threads, and a smaller amount of fiber length degradation is significant. Compression molding is also suitable for the production of super-large matrix shapes whose dimensions exceed the capabilities of extrusion technology. In addition, compared to other methods such as transfer molding and injection molding, it is one of the lowest cost molding methods. In addition, it wastes relatively little material and has advantages when using expensive compounds. Learn more about compression molding vs. injection molding here.
Disadvantages of compression molding
-
1. At present, it is not suitable for molding complex parts with depressions, side slopes or small holes.
-
2. Burrs must be trimmed manually. This is caused by several different factors, and MDC will minimize the excess flash.
-
3. For thermosetting plastics, when the molded products have slight defects, they are often unable to be recycled.
-
4. Tooling costs are often high, but the cost of compression molded parts is very low after mass production.
Advantages of compression molding
-
1. Suitable for mass production, short cycle moulding times and high efficiency;
-
2. Lowest cost molding methods, the loss of raw materials and the mold wear is small, and the maintenance cost of the mold is low.
-
3. It can be used to form large flat products. High dimensional accuracy, small shrinkage, low internal stress, high strength, the mechanical properties are relatively stable. The surface is smooth without secondary modification.
-
4. Advanced composite materials are used to ensure better mechanical properties of the products.
Learn more about the pros and cons of compression molding
Compression Molding Process Parameters
The quality performance of plastic parts is influenced by the performance of plastic raw materials, mold structure and size, but also related to the development and control of molding process parameters. When we use the compression moulding method, we must consider the following 7 factors:
-
material. the choice of material is very important.The technique is often used for moulding of glass fiber reinforced parts and high pressure is often used. Wear resistance, strength and hardness are required from the mould material.
-
shape, the choice of shape is crucial for the subsequent production
-
pressure. Molding pressure refers to the unit pressure of the press on the projected area of the plastic part during compression molding. Its role is to force the plastic melt to flow and fill the mold cavity, to avoid bubbles, loose structure and other defects inside the plastic part due to low molecular volatiles, to ensure that the plastic part has a fixed shape and size, to prevent deformation, and to improve the inherent quality.
-
temperature. Molding temperature refers to the temperature of the mold required for pressing. At this temperature, the plastic melt flows in the mold cavity, fills the cavity and cures. The mold temperature is not equal to the temperature of the plastic melt in the cavity. If the molding temperature is too high, the curing time will be short, but it will cause difficulties in filling the mold, making the surface of the plastic parts dull and lusterless, and even swelling, deformation and cracking will occur. Molding temperature is too low, the curing time is slow, the molding time is long. If you want to know more about compression molding temperature, please click here.
-
partial thickness
-
cycle time. Thermosetting plastics compression molding, need to maintain a certain temperature and pressure for a certain period of time, in order to fully cross-link curing, become a good plastic parts, this time is called compression time. Compression time is related to the type of plastic (resin type, volatile content, etc.), the shape of the plastic part, the process conditions of compression molding (temperature, pressure) and the operation steps (whether exhaust, pre-pressure, preheating). The length of the compression time has a significant impact on the performance of the plastic part. Compression time is too short, the plastic hardening is not enough, the appearance of poor quality plastic parts, mechanical properties decline, easy to deformation. Properly increase the compression time, can reduce the shrinkage of plastic parts, improve its heat resistance and other physical and chemical properties. But the compression time is too long, not only will reduce productivity, but also make the plastic shrinkage too much, the internal stress increases, the plastic part is easy to rupture. General phenolic plastic compression time for l ~ 2min, silicone plastic for 2 ~ 7min.
Application of compression molding:
What is compression moulding used for? Compression molding is first used to make composite parts for metal replacement applications, and is often used to make larger flat or moderately curved parts. This molding method is widely used in automotive components, electrical, and architectural fields, such as automotive hoods, automotive door panels, electrical equipment housings, and building templates.



China compression moulding company
As China compression mold company, MDC Mould provides various compression molding solutions and provide complete compression mold design services and manufacture. Compression moulding is one of MDC largest business. For many years, MDC has specialized in SMC moulding, BMC moulding, GMT moulding, LFT moulding. We have advanced milling machines and professional engineers. Making high-quality moulds is our goal.
MDC has mastered and innovated the molding process, analyzed the characteristics of the materials and the requirements of the products, and considered the applied pressure, temperature, time and other factors to ensure the uniform flow of the materials in the cavity of mold and fill the gaps to obtain the perfect products.The following are some of MDC's experiences with compression moulding:
-
1: Maintain pressure during cooling to avoid uneven surface.
-
2: Smooth surface mould with fast cooling rate can prevent the product from sticking to the mould..
-
3: ...
MDC Mold will always provide support to our customers. We are honoured to receive the Best Supplier Award from TATA Group in 2019. If anyone has requirements for compression moulds, please contact us.


 Overview of Compression Molding
Overview of Compression Molding







